Introduction
Gymnastics is a sport that demands an exceptional level of strength, agility, and precision. While the focus has traditionally been on bodyweight exercises, there has been increasing interest in the role of weightlifting in a gymnast’s training regimen. This article explores whether gymnasts lift weights, the benefits and drawbacks of weightlifting for gymnasts, and expert opinions on this subject. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of the intersection between gymnastics and weightlifting.
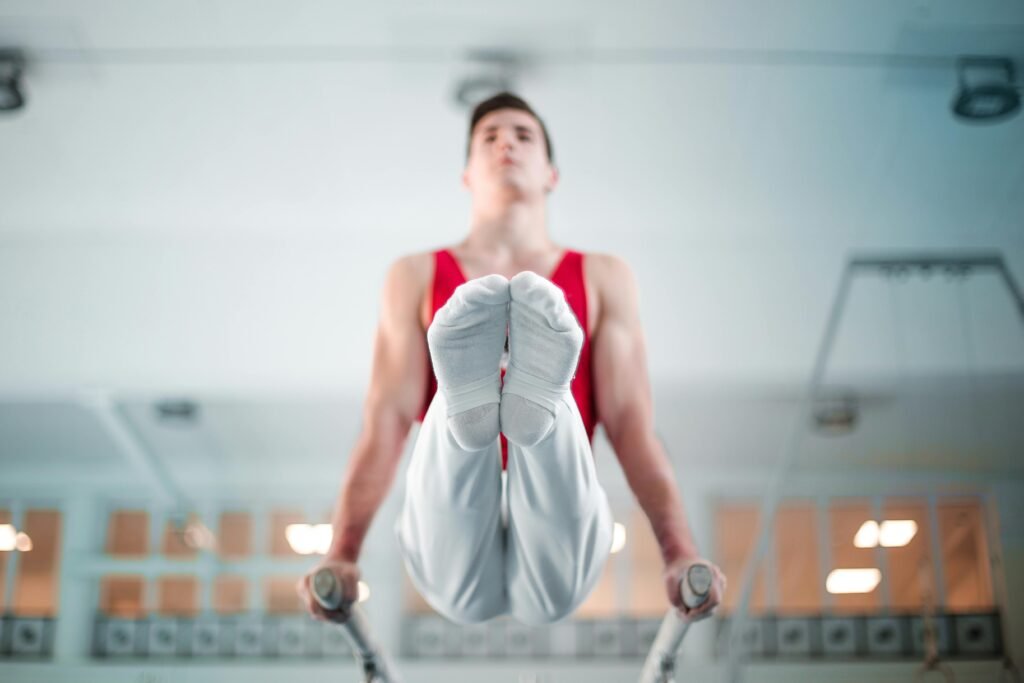

The Role of Strength in Gymnastics
Strength plays a critical role in gymnastics, influencing performance, injury prevention, and overall athletic development. Gymnasts require a unique blend of strength that includes explosive power, muscular endurance, and dynamic stability.
Importance of Strength Training for Gymnasts
Strength training is fundamental to a gymnast’s success. It enhances their ability to perform complex skills, maintains muscle balance, and reduces the risk of injuries. Proper strength training can improve a gymnast’s ability to execute high-flying maneuvers, support body positions, and land safely from jumps and flips.
Types of Strength Required in Gymnastics
Gymnasts need various types of strength, including:
- Explosive Strength: For powerful takeoffs and quick movements.
- Isometric Strength: To hold static positions like handstands and iron crosses.
- Muscular Endurance: To perform routines that require sustained effort.
Traditional Gymnastics Training
Gymnasts have long relied on bodyweight exercises to develop the necessary strength and flexibility for their sport. These exercises are tailored to mimic the movements and positions encountered in gymnastics routines.
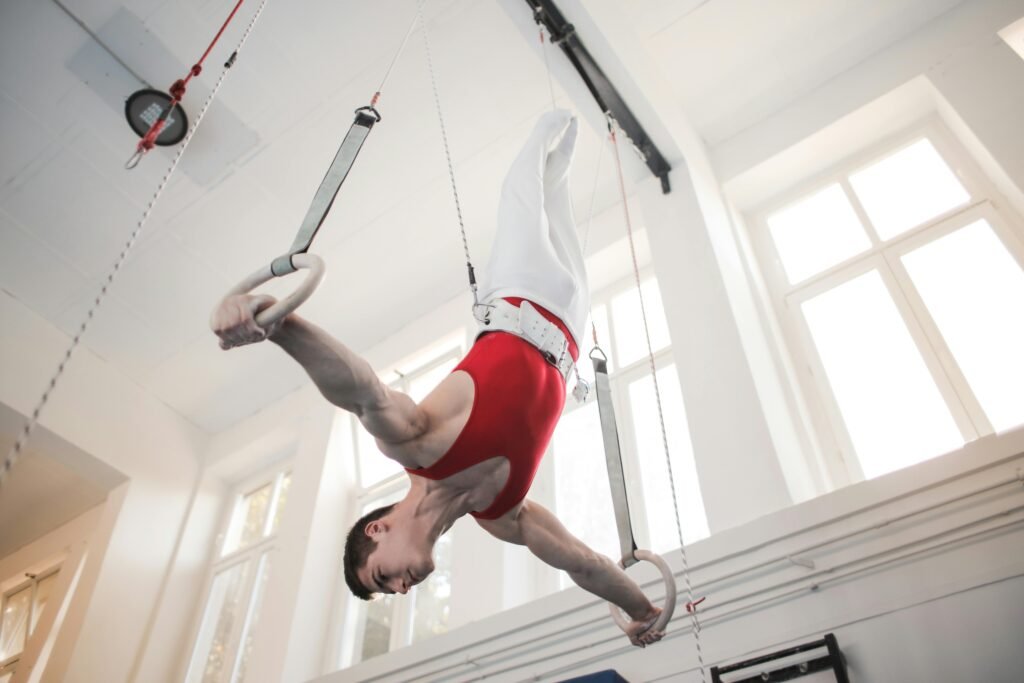

Bodyweight Exercises
Bodyweight exercises such as push-ups, pull-ups, dips, and planks are staples in a gymnast’s training. These exercises build functional strength, directly translating to improved performance in gymnastic events. Gymnasts often perform these exercises with high repetitions to enhance muscular endurance and control.
Flexibility and Endurance Training
In addition to strength, flexibility and endurance are vital components of a gymnast’s training. Stretching routines and flexibility exercises help maintain a wide range of motion, crucial for executing splits, leaps, and other maneuvers. Endurance training, such as cardio workouts, ensures that gymnasts can sustain energy levels throughout their routines.
Incorporation of Weightlifting in Gymnastics
The incorporation of weightlifting into gymnastics training has evolved over time. While traditional methods focused solely on bodyweight exercises, modern approaches have recognized the benefits of weightlifting for gymnasts.
History and Evolution
Historically, weightlifting was not a common practice among gymnasts. The primary concern was that weightlifting might negatively impact flexibility and agility. However, over the past few decades, sports science has demonstrated that weightlifting, when done correctly, can complement a gymnast’s training by enhancing strength and power without compromising flexibility.
Current Practices
Today, many elite gymnasts incorporate weightlifting into their training regimens. Weightlifting is used strategically to target specific muscle groups, improve overall strength, and enhance performance. Exercises such as squats, deadlifts, and Olympic lifts are commonly included, with a focus on proper technique and controlled movements to prevent injury.
Benefits of Weightlifting for Gymnasts
Weightlifting offers several benefits that can significantly enhance a gymnast’s performance. By integrating weightlifting into their routines, gymnasts can achieve greater power, stability, and injury resistance.

Increased Power and Explosiveness
Weightlifting helps gymnasts develop explosive power, which is essential for executing high jumps, quick rotations, and dynamic movements. Exercises like cleans and snatches train the muscles to generate force rapidly, translating to more powerful performances on the floor and apparatus.
Enhanced Muscle Balance and Injury Prevention
Weightlifting promotes balanced muscle development, addressing any asymmetries that may arise from repetitive gymnastics movements. This balanced strength reduces the risk of overuse injuries and improves joint stability. Additionally, stronger muscles and connective tissues provide better support for the intense demands placed on the body during gymnastics routines.
Weightlifting vs. Bodyweight Training
While both weightlifting and bodyweight training offer unique benefits, it’s essential to understand their differences and how they can complement each other in a gymnast’s training program.
Pros and Cons of Weightlifting
Pros:
- Increases overall strength and power.
- Enhances muscle balance and joint stability.
- Reduces injury risk.
Cons:
- Requires careful supervision and proper technique.
- Potential risk of injury if not performed correctly.
- May require additional recovery time.
Pros and Cons of Bodyweight Training
Pros:
- Develops functional strength specific to gymnastics movements.
- Improves muscular endurance and control.
- Can be performed anywhere, without special equipment.
Cons:
- May not provide enough resistance for advanced strength gains.
- Can lead to muscle imbalances if not varied.
- Limited to bodyweight, which might not be challenging enough for all muscle groups.
Famous Gymnasts Who Lift Weights
Many renowned gymnasts have incorporated weightlifting into their training regimens, crediting it for their enhanced performance and longevity in the sport.
Case Studies and Testimonials
Gymnasts like Simone Biles and Kohei Uchimura have shared insights into their training routines, highlighting the role of weightlifting in achieving their remarkable feats. These athletes emphasize that weightlifting helps them maintain peak physical condition, allowing them to perform at the highest level consistently.
Expert Opinions on Gymnasts Lifting Weights
To understand the broader implications of weightlifting in gymnastics, it’s valuable to consider the perspectives of coaches and sports scientists.
Coaches’ Perspectives
Many gymnastics coaches advocate for incorporating weightlifting into training programs. They believe that weightlifting can enhance strength and power while providing a well-rounded physical foundation. However, they stress the importance of tailored programs that address the unique needs of each gymnast.
Sports Scientists’ Insights
Sports scientists support the integration of weightlifting, citing research that demonstrates its benefits for athletic performance and injury prevention. They emphasize that weightlifting should be approached with a focus on proper technique, individualized programming, and gradual progression to maximize benefits and minimize risks.
Common Weightlifting Exercises for Gymnasts
Certain weightlifting exercises are particularly beneficial for gymnasts, targeting key muscle groups and enhancing overall strength and performance.
Lower Body Exercises
Squats: Squats strengthen the lower body, improving leg power and stability.
Deadlifts: Deadlifts develop posterior chain strength, essential for explosive movements.
Lunges: Lunges enhance balance and unilateral leg strength.
Upper Body Exercises
Pull-Ups: Pull-ups build upper body and grip strength, crucial for apparatus work.
Bench Press: Bench press improves chest, shoulder, and triceps strength.
Shoulder Press: Shoulder press enhances overhead strength and stability.

Safety and Precautions
While weightlifting offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to prioritize safety and adopt best practices to prevent injuries.
Proper Technique and Form
Proper technique and form are paramount in weightlifting. Gymnasts should receive guidance from experienced coaches to ensure they execute exercises correctly. This minimizes the risk of injury and maximizes the effectiveness of the workouts.
Avoiding Overtraining
Gymnasts should balance weightlifting with their regular training routines to avoid overtraining. Adequate rest and recovery are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing burnout.



Its like you read my mind You appear to know so much about this like you wrote the book in it or something I think that you can do with a few pics to drive the message home a little bit but other than that this is fantastic blog A great read Ill certainly be back